All Activity
- Past hour
-
svc_kms started following How to collect and send false positive emails with headers from KSE to Kaspersky Lab [Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Server] , How a Distribution Point for a host is selected [KSC for Windows] , Sizing recommendations for KSC for connecting VDI hosts [KSC for Windows] and 7 others
-
How a Distribution Point for a host is selected [KSC for Windows]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Security Center's Kaspersky Security Center Community
Advice and Solutions (Forum Knowledgebase) Disclaimer. Read before using materials. If two different update agents on a PC are assigned in different ways: To an administration group. Based on a network location. Which one will have a higher priority for the PC? Among the update agents assigned to administration groups, the one assigned to the administration group, that is closest to the target host in the group hierarchy, has the higher priority. If the update agents are assigned to the same group, they have an equal priority. The priority of update agents assigned based on the network location is equal to the priority of the nearest update agent in the group hierarchy. If two update agents have the same priority, the one, the route to which is closer in the number of passed routers, is selected. If two update agents have the same priority and the network distance to them is the same, the agent is selected randomly. -
Advice and Solutions (Forum Knowledgebase) Disclaimer. Read before using materials. Dynamic hosts require more KSC resources than regular hosts. When a new host is connected to KSC (and the dynamic host is considered new), an icon and a new entry in the database are created, full synchronization with the agent is performed, and the host moved to a group. When the host is deleted, all information about it is deleted as well. These operations consume a lot of KSC resources, while static hosts require them to be performed only once. Recommended sizing (no more than 20 000 VDI hosts) may not be fully and correctly loaded. In industrial use, for each icon the following network lists are created: - hardware - installed software - detected vulnerabilities - events and lists of executable files of the Application control component. Size of these lists directly affects KSC performance as well as SQL server performance when performing internal procedures, and the load may grow in the non-linear way. If the use of the solution with your policy settings, environment and virtual desktop properties shows moderate consumption of resources during standard operations, then the number of managed VDI hosts can be increased up to the limit of resources available in the current configuration. Consumption of 80% of memory and 75-80% of available cores is considered moderate.
-
Problem After "Nessus" vulnerability scanning on Central node 4.0 servers, you may see the following: Ports: 22-tcp Description: The remote SSH server is configured to allow key exchange algorithms which are considered weak. This is based on the IETF draft document Key Exchange (KEX) Method Updates and Recommendations for Secure Shell (SSH) draft-ietf-curdle-ssh-kex-sha2-20. Section 4 lists guidance on key exchange algorithms that SHOULD NOT and MUST NOT be enabled. This includes: diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1 diffie-hellman-group1-sha1 gss-gex-sha1-* gss-group1-sha1-* gss-group14-sha1-* rsa1024-sha1 This is about a IETF proposed standard (formerly a draft) introduced in January 2022 after KATA 4.0 release. These IETF recommendations are addressed in KATA version 5.0. Solution Disclaimer This security hardening procedure is done "at your own risk", at the present moment we don't suggest to apply it preemptively. KATA 4.0 has OpenSSH_7.4p1, OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips. This version supports newer Key Exchange (KEx) algorithms, so disabling weaker ones doesn't pose a problem. However, the list of key exchange algorithms that are accepted by GSSAPI key exchange for this version have only the ones that are named weak by the IETF draft, man SSHD_CONFIG(5) says: GSSAPIKexAlgorithms The list of key exchange algorithms that are accepted by GSSAPI key exchange. Possible values are gss-gex-sha1-, gss-group1-sha1-, gss-group14-sha1- Therefore, the only option to remove these in OpenSSH_7.4p1, is to disable GSSAPI key exchange. GSSAPI however is used by Kerberos authentification, so the possible impact is that Kerberos integration may be affected after these changes. So, in order to achieve the desired result: Open /etc/ssh/shh_config #vi /etc/ssh/shh_config Locate the line GSSAPIAuthentication yes Change it to "no": GSSAPIAuthentication no Add (or uncomment) the line GSSAPIKeyExchange no Add the line defining the KEX algorithms to be used. These are all the algorithms supported by existing version of OpenSSL except the weak ones: KexAlgorithms diffie-hellman-group14-sha256,diffie-hellman-group16-sha512,diffie-hellman-group18-sha512,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,curve25519-sha256,curve25519-sha256@libssh.org Exit vi and save :wq! Restart sshd #systemctl restart sshd Confirm applied changes by listing the loaded gssapi settings and KEX algorithms. # sshd -T | grep kex # sshd -T | grep gssapi
-
Access to the Microsoft quarantine is carried out immediately after the issuance of the consent. Additional quarantine access accounts, that were subject to the MFA restriction in the previous versions, are no longer required for quarantine access. The connection is carried out using the application to which the consent is issued.
-
Why are emails detected by Microsoft Exchange Online not being detected by KS365? Because "first come, first served"? Yes. In more than 95% of cases, Microsoft Exchange anti-malware and anti-spam filters are processing all objects before KS4O365. That being said, all the detections performed by our application are actually detections of mail flow that has already been scanned by Microsoft filters if they are not disabled. If some email was already scanned and quarantined by Microsoft, then we do not receive it for scanning, as it was already done on the Microsoft side.
-
If multiple e-mails are selected in Security for Microsoft Office 365, they cannot be saved to disk. You can only save them one by one.
-
If anti-spam detects an e-mail as not definitely categorized as clean, it moves the e-mail to the "Temporary Quarantine" for 50 minutes to re-scan it with updated anti-spam databases. If upon after this 50 minutes' time the e-mail is not defined as spam, it is released automatically without any interaction with the user. The administrator has an option to manually release such e-mails from "Temporary Quarantine" before the 50 minute period ends. At the same time, the e-mail will remain in quarantine with the status "Released".
-
Is there any capacity limit of mails in the Quarantine zone? If any, can we modify it? Unfortunately, there is no possibility to customize this setting per user, it is hardcoded in the product (30 days for objects in the backup and 92 days for statistics). Is there any limit on the number of emails that can be stored in the Quarantine? On the KS4O365 side, there isn't a limit to the number of emails that can be saved in the backup. KS4O365 stores only metadata information about the emails in the backup, which is quite small in comparison to the email itself. Whereas the backup emails themselves are stored in the mailbox (in a hidden folder) on the Exchange online server that hosts mailboxes. When the object is restored from the Quarantine, the email from a hidden folder is simply moved to the inbox. That being said, the only limit that can be identified in the said scenario is the one from the Exchange online itself (the size of the mailbox for a particular user). I.e. if the total amount of emails in the inbox + emails in the backup will hit the limit of the free space in the Exchange Online mailbox, then the you will need to increase the size of the mailbox or remove the exceeding emails, etc. The emails from quarantine can be deleted from the Quarantine tab of the console, there you can also sort by date to delete the old ones.
-
Scenario: Phishing links are detected but some emails are allowed through, even though the selected Action is Move to Junk Email folder . Solution: The original e-mail was already located in the Junk folder when our product started to scan it. The "Allow through" action was performed, in this case it means that we've added the phishing tag to the e-mail and left it in the Junk folder. Most likely this e-mail was detected by some third-party anti-malware/phishing solution (Microsoft anti-malware filters in EWS, for example) and was moved to Junk, then we've scanned it and there was nothing to do with it except adding the tag to it.
-
In order to send messages from backup with headings without saving them, please navigate to:
-
Version: Kaspersky Security for Exchange 9.5.10000.64, 9.6.96 Scenario In Kaspersky Security 9.0 for Microsoft Exchange Servers there's the following error event: "AM Error Kernel: The Anti-Virus (Anti-Spam) module has been switched to limited scan mode for next 30 minutes. Some objects may be skipped without being scanned." The same error message appears on the KSE console: Solution Sometimes Exchange tries to give KSE more emails to check than KSE is able to to check. In order to prevent delays in mail delivery, the anti-virus or/and anti-spam engine switches to a special mode of operation called "Limited scan mode". This mode lasts for 30 minutes. During this period, some emails may be skipped for checking. The transition to normal mode is carried out automatically after the time specified above. You can find out about this mode of operation in our Online Help: https://support.kaspersky.com/KS4Exchange/9.6/en-US/28854.htm https://support.kaspersky.com/KS4Exchange/9.6/en-US/99915.htm https://support.kaspersky.com/KS4Exchange/9.6/en-US/28871.htm
-
Scenario Kaspersky Security for Exchange installation failed with the following error: "Failed to grant rights to run under a different name (impersonation) for Kse Watchdog Service". Solution If you get the error message about impersonation, execute the following command in PowerShell: Add-PsSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.E2010 Remove-ManagementRoleAssignment KSE_IMPERSONATION -Confirm:$False Press the Retry button.
-
Advice and Solutions (Forum Knowledgebase) Disclaimer. Read before using materials. Version: Kaspersky Security for Exchange 9.0 MR5 (9.5.10000.64) Scenario The following error message appears: "Access denied. To manage application features, the user's account must be added to one of the following Active Directory groups: KSE Administrators KSE AV Security Officers KSE AV Operators KSE Security Officers." Solution This error means that the account under which the KSE management console is running is not part of any of the KSE management groups listed above in the error text. The user needs to decide what role the user’s account will perform and include this account in the corresponding KSE group created in their Active Directory (AD). You can learn more about the roles in our Online Help: https://support.kaspersky.com/help/KS4Exchange/9.5/en-US/81511.htm
-
Version: KSE for Microsoft Exchange Server versions 9.5.10000.64, 9.6.96. Scenario: We have established a workaround to a problem with invalid SQL server parameters during its installation. An error about invalid SQL server parameters occurred during the installation: "The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct, and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections. Error 26 - Error Locating Server/Instance Specified". We have found the following information from installation log: Installation log showed the SQL server "CRATER\SQLEXPRESS" was used for the installation: We found that the configuration file "BackendDatabaseConfiguration*.config" which was used for configuring the SQL server was using the server name "CRATER". Solution: If you're sure that "CRATER\SQLEXPRESS" is the real name of the SQL server, replace "CRATER" in the SQL server name by "CRATER\SQLEXPRESS" in the following objects: 1. "X:\%KSE_Folder%\Configuration\BackendDatabaseConfiguration*.config" file. If there are several such files in this folder, do it for all of them. 2. In the system registry "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Server". Parameter is BackendSqlServerName. Start the upgrade again.
-
In most cases the issue is related to processing downloaded bases on the server drive. Databases are downloaded from our sites successfully, but the problem appears during compiling and copying the downloaded bases locally on the KSE server. Such behavior may be caused by the following: Not configured exclusions for KSE in Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Endpoint Security. Other utilities (backup, for example), that may interfere with the file processing. Incorrect operation of the delete function on high-speed drives, for example, SSD drives. Solution: 1. Configure Kaspersky Security for Windows Server or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for correct simultaneous work with KSE. Completely exclude the KSE folder, all subfolders and KSE processes from the scan scope: Kavscmesrv.exe Antiphishing.OutprocScanner.exe Antispam.OutprocScanner.exe Antivirus.OutprocScanner.exe Kse.Ksn.exe Kse.Licensing.exe Kse.Updater.exe 2. Set the startup type of KSE service to manual. 3. Stop the KSE service. 4. If issue is related to corrupted AS bases, delete all contents from the folders: C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\as\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\ap\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\ap\cache If issue is related to corrupted AV bases, delete all contents from the folders: C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\av\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\av\cache If issue is related to corrupted AS and AV bases, delete all contents from the all folders: C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\as\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\ap\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\ap\cache C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\av\bases C:\Program Files (x86)\Kaspersky Lab\Kaspersky Security for Microsoft Exchange Servers\data\bases\av\cache 5. Set the startup type of KSE service back to automatic/ automatic (Delayed Start), as it was before adjustment at step 2. 6. Start the KSE service. 7. Update anti-spam or/and anti-virus bases manually through KSE Management Console. 8. If the issue persists, contact Kaspersky Support.
-
Вы самолично наблюдали за процессом связывания? Решили уже путем смены драйвера в настройках. По крайней мере, так гласит инструкция. С чего они должны что-то делать еще - неясно.
-
Advice and Solutions (Forum Knowledgebase) Disclaimer. Read before using materials. This article is about Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows (KES for Windows) This informational message does not mean that Self-Defense accuses any process of being under malware attack, it proactively blocks certain operations that could pose a potential threat to processes. The number of events depends on the activity of applications that inhabit the system, especially from their periodic activities, polls on a timer, on emerging events, and so on. The event in the reports is informational - it can be simply disabled it in the settings. It's not expected to react to these events. More specifically, it's usually the update programs and VMWare services try to access application processes. The update programs want to restart all processes when the update is finished so that they don't have to reboot the system. But KES doesn't allow them to restart our processes. The applications causing these events: Microsoft Edge Update Google Installer Windows installer VMware Authorization Service Host Process for Windows Services Client Server Runtime Process It is normal for such a request to fail, and this should not be a concern. These events can be turned off in active KES policy: General settings→Interface→Notifications: informational messages→Self-Defense restricted access to the protected resource.
-
How to store MS BitLocker recovery keys in Active Directory [KES for Windows]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Endpoint Security's KES for Windows
If you want to store FDE encryption keys in Active Directory, this is possible if BitLocker encryption is used. In order to transfer and store the recovery passwords (keys) in Active Directory, it is necessary to: 1. Enable the “Choose how BitLocker-protected operating system drives can be recovered” group policy https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/information-protection/bitlocker/bitlocker-group-policy-settings#bkmk-rec1 for target computers and configure saving BitLocker recovery information to Active Directory Domain Services there. Here is the target policy in the gpedit.msc snap-in on the computer where encryption is planned to be enabled: 2. Install ‘BitLocker Recovery Password Viewer’ feature on the computer with the AD DS Domain Service running: This functionality does not apply to Kaspersky products by design, but in theory it can be used in parallel with MS BitLocker Drive Encryption technology deployed by means of KES BitLocker management (i.e. through Kaspersky product). In this case, after encryption starts the recovery data will be transferred and stored both in AD and on the KSC server. We highly do not recommend applying any settings via the BitLocker (GPO) policies (the recommended configuration is "Not configured" for all policies located in the [Computer configuration / Administrative Templates / Windows Components / BitLocker Drive Encryption] node and below), because they can prevent from deploying bitlocker related settings through Kaspersky product policy. It will lead to an error in applying BitLocker Drive Encryption ‘Encrypt all hard drives’ policy and the inability to encrypt the disk as a result. -
Completely exclude the KSE folder with all its subfolders and all KSE processes from the scan scope: Kavscmesrv.exe Antiphishing.OutprocScanner.exe Antispam.OutprocScanner.exe Antivirus.OutprocScanner.exe Kse.Ksn.exe Kse.Licensing.exe Kse.Updater.exe
-
How to check Adaptive Anomaly Control (AAC) [KES for Windows]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Endpoint Security's KES for Windows
To check Block action: Specify Block actions for all rules in the group Activity of script engines and frameworks. Extract files from the archive and start the scripts. All scripts should be blocked, popup about it should be shown. There will be new records about blockings in the local report, events and AAC report in KSC console. To check Smart action: Host where KES is installed is under the policy applied. Specify Smart mode for all rules in the group Activity of script engines and frameworks. Extract files from the archive and start any script. Open KSC → Advanced → Repositories → Triggering of rules in Smart Training State. Check that new record is shown there. There will be no info about this detection in local report, KSC reports or in the events. After two weeks, if there are no new detections for this rule, the rule will automatically change to Smart Blocking mode. If this rule is detected again, the learning period will be extended. -
Device Control errors [KES for Windows]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Endpoint Security's KES for Windows
Issue Sometimes Device Control errors in KES may occur. For example, hard drives are wrongly blocked when USB device blocking is enabled, or flash drive blocking is not happening although the policies require to do so. In some cases, the reason for erroneous blocking is that the operating system (OS) is incorrectly identifying the device type. Solution As an example, if the policies prohibit access to flash drives, but this rule does not always work, you can check the following: Go to Device manager and check the Removal policy parameter. The parameter value must be 2 or 3 if the OS has correctly detected the flash drive. If the parameter value is any other value other than 2 or 3, then the OS considers the attached device to be non-removable. Based on this data, KES decides to allow access to the device and not block it, and then informs the user. Below we have added all the possible values and their descriptions which the Removal policy parameter can have: Removal policy 00000001 - ExpectNoRemoval (cannot be extracted at all) Removal policy 00000002 - ExpectOrderlyRemoval Removal policy 00000003 – ExpectSurpriseRemoval Conclusion If the flash drive is not blocked by KES and the removal policy parameter has a value other than 2 or 3, it means that the OS has detected the drive incorrectly. Thus, this is not a bug in the Kaspersky app. -
Info about KES in registry [KES for Windows]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Endpoint Security's KES for Windows
How to check if KES is installed, its state (running or not) and bases version via registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\KasperskyLab\Components\34\1103\1.0.0.0\Statistics\AVState More information about these registry keys is available in Online Help: https://support.kaspersky.com/ksc14/3644. Obtaining information from the registry is for familiarization purposes only. KESCLI commands method supported by developers: Managing the application from the command line > KESCLI commands > GetRealTimeProtectionState. File Threat Protection status https://support.kaspersky.com/help/KESWin/12.2/en-US/213719.htm Managing the application from the command line > KESCLI commands > GetDefinitionState. Determining the update completion time https://support.kaspersky.com/help/KESWin/12.2/en-US/213724.htm Information in following registry is created by network agent (NA). Information will be deleted before OS shutdown and will be created after OS boot. There is a delay (120s) for NA service start. So if you need to get the state of KES immediately after OS boot, use KESCLI. -
This only applies to KSC 14.2 and below Problem Remote installation tasks finishes with uninformative errors: Setup process error: Unknown error. (126) Setup process error: Unknown error. (2) Solution 1. Create 3rd party installation package (Create installation package -> Create an installation package for the specified executable file.) 2. Specify executable file, for example script.sh 3. Locate this package folder in KSC storage, by default %ProgramData%\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\share\Packages\(package_name) 4. Edit .\(package_name)\executable_package.kpd: remove exec\ from Executable path, add DontWrap=1 option. Setup section should read the following: executable_package.kpd [Setup] Executable=script.sh DontWrap=1 Params= 5. Edit .\(package_name)\exec\executable_package.kpd: remove exec\ from Executable path, add DontWrap=1 option. Setup section should read the following: exec\executable_package.kpd [Setup] Executable=script.sh DontWrap=1 Params= 6. Copy .\(package_name)\exec\script.sh to .\(package_name)\script.sh 7. Check that in package Settings, "Executable file" changed from exec\script.sh to script.sh 8. Use this package in "install application remotely" task
-
KATA: KEA tasks FAQ [KATA/KEDRE]
svc_kms posted a blog entry in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack & EDR Expert's KATA & KEDR Expert community articles
What is the default synchronization period between KEA and CN? Sync period (which is every X minutes) for KEA is configurable in KEA policy. Default synchronization period is 300 sec (5 min). The same period applies to LENA. What is the isolation workflow? In KATA CN creates task for host isolation. KEA receives an 'isolate' command from the Central Node during synchronization . An agent turns on host isolation with exclusions configured in KEA policy. At the next sync time (after X minutes) the agent sends the results of isolation to the Central Node . When isolation is turned on isolated host connected to the Central Node, you can view the telemetry from this host and execute other tasks. Is it OK that isolation takes up to 10 minutes? Yes, see previous two sentences for explanation. It takes up to 5 minutes to sync a task with the host when default settings are applied. To sync the status back to CN we need another 5 minutes. What will happen if the IOC scan didn't finish within Maximum scan duration. Will it resume next time or it will terminate? IOC scan task starts as scheduled and then terminates upon reaching the Maximum scan duration even if it hasn'tt finished yet. The next scheduled time the scan task starts from the beginning. How to determine whether the specified time is enough to complete the scan? Experimentally. The default scan is a full scan, are there any options to set a custom scan? IOC scan task is not configurable in KATA, thus there is no way to set a custom scan. -
This works an all KATA CN versions from 3.6.1 to 5.1 You can execute the queries below with Curl to get the text representation of agent status. SSO login and password must be used, limit of 200 entries is used in the example query. JSONs with agent status curl -s --output /dev/null -c ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"username":"SSO","password":"MYPASSWORD","local":false}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/userLogin && curl -s -b ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Referer: https://KATACN:8443/katap/' -d '{"limit":200,"offset":0}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/hostsAgentActivity | python -m json.tool This query can be customized further to get lists of hostnames, IPs etc: List of unique agents hostnames curl -s --output /dev/null -c ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"username":"SSO","password":"MYPASSWORD","local":false}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/userLogin && curl -s -b ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Referer: https://KATACN:8443/katap/' -d '{"limit":200,"offset":0}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/hostsAgentActivity | python -m json.tool | grep hostname | awk -F\" '{print $4}' | sort | uniq List of unique agents hostnames curl -s --output /dev/null -c ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"username":"SSO","password":"MYPASSWORD","local":false}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/userLogin && curl -s -b ./cookie -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Referer: https://KATACN:8443/katap/' -d '{"limit":200,"offset":0}' https://KATACN:8443/apt/api/hostsAgentActivity | python -m json.tool | grep \"ip\" | awk -F\" '{print $4}' | sort -n | uniq

Kaspersky Plus
Güvenlik. Performans. Gizlilik. Hepsi kullanımı kolay tek bir uygulamada.

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Küçük ölçekli işletmenizi kolayca koruyun

Kaspersky Password Manager
Parolalarınız ve belgeleriniz her zaman elinizin altında

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Unkomplizierter Schutz für kleine Unternehmen

Premiumversion
Kaspersky Safe Kids
Behalten Sie Ihre Kinder im Auge, auch wenn Sie nicht in der Nähe sind
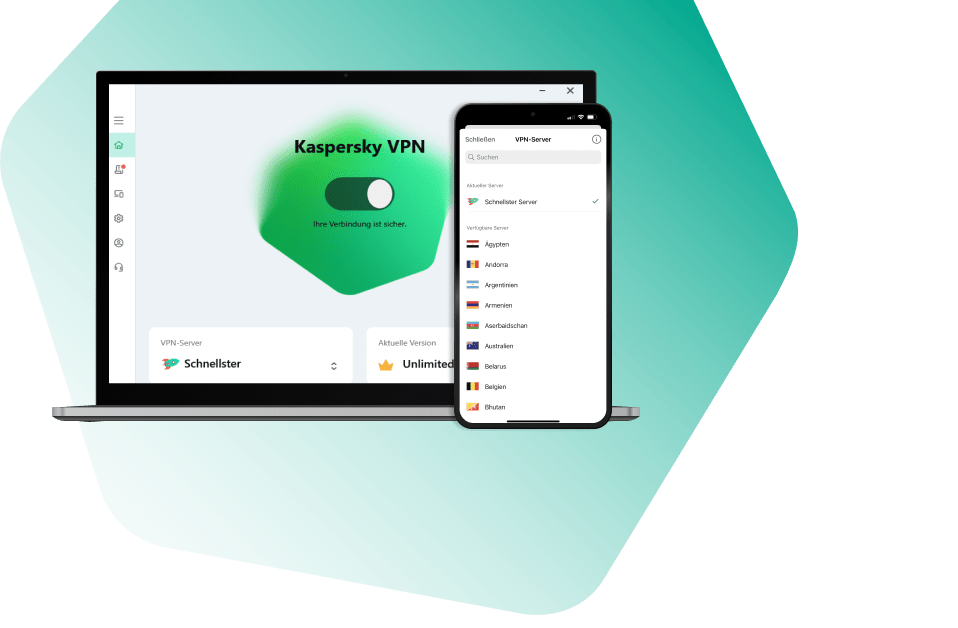
Kaspersky VPN Secure Connection
Sicher. Privat. Außergewöhnlich schnell. So sollte Internet sein.

Kaspersky Standard
Mejora la protección con el optimizador del rendimiento del dispositivo

Kaspersky Plus
Seguridad. Rendimiento. Privacidad. Todo en una única aplicación fácil de usar.

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Proteja fácilmente su pequeña empresa

Versión premium
Kaspersky Safe Kids
Supervisa a tus hijos, incluso cuando no estés con ellos

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Protégez votre PME sans effort

Kaspersky Plus
Combina recursos de segurança, desempenho e privacidade em um aplicativo

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Proteja a sua pequena empresa sem esforço

Kaspersky Premium
Proteção completa para seus dispositivos, privacidade online e identidade

Versão Premium
Kaspersky Safe Kids
Fique de olho nas crianças, mesmo quando não estiver por perto
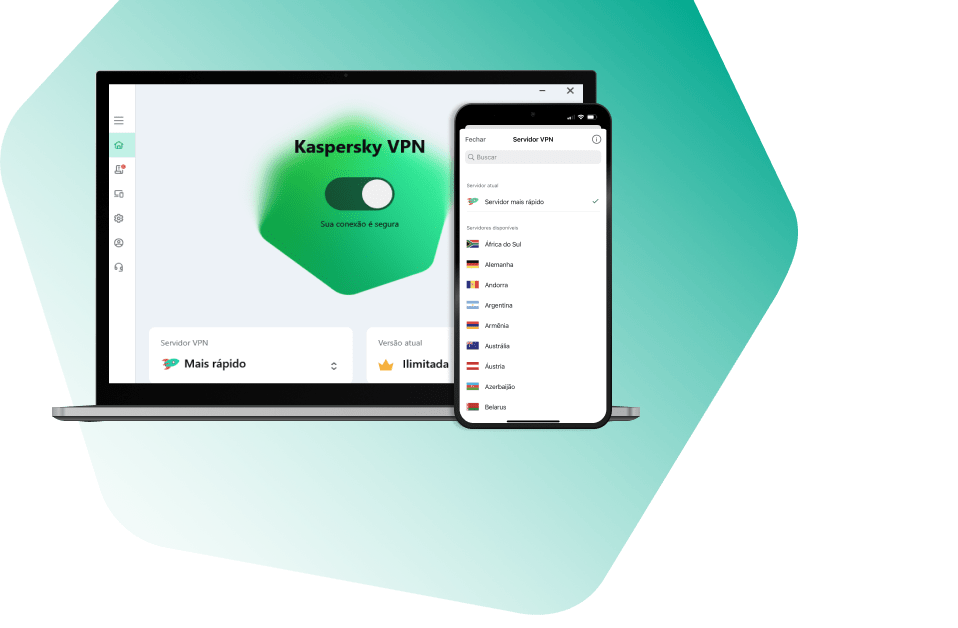
Kaspersky VPN Secure Connection
Segura. Privada. Excepcionalmente rápida. Como a internet deveria ser.

Kaspersky Standard
Protezione avanzata con ottimizzazione delle prestazioni dei dispositivi

Kaspersky Small Office Security
Protezione immediata delle piccole aziende

Versione premium
Kaspersky Safe Kids
Accertati che i tuoi figli siano al sicuro, anche quando non sei con loro

Kaspersky Secure Connection
Надёжное шифрование и защита данных — даже в открытых Wi Fi сетях








